Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS): A group of safety systems that monitor vehicle performance and the surrounding environment. ADAS alerts the driver of potentially hazardous conditions, and some (such as automatic emergency braking) can take corrective action if the driver fails to respond appropriately.
Alternating Current (AC): An electric current that regularly changes direction. It is the standard electrical current in homes.
Amp: Short for ampere, an amp is a unit of electrical current. It measures how much electricity is passing through a point at a given time. In regard to EVs, it is used to describe chargers. Higher amperage generally means faster charging.
Autonomous Vehicle: A car that uses advanced technology to accelerate, brake and steer itself.
Batteries: The source of energy in EVs. They are recharged by connecting the vehicle to an electrical outlet or charging station.
Battery Electric Vehicle (EV): A vehicle powered entirely by an electric battery and uses one or more electric motors for propulsion.
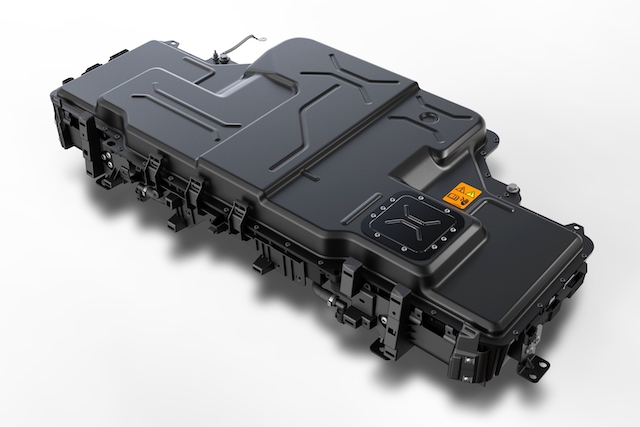

Battery Pack: The entirety of an EV’s battery. It is composed of thousands of battery cells grouped together in battery modules, all contained in a protective structural enclosure.
Carbon Footprint: The combined greenhouse gas emissions generated by a person, place or thing.
Charging: Connecting an EV to an external power source to replenish the battery power.
Charging Station: Publicly available locations where EV owners can charge their vehicle.
Charging Point: Any charging device, public or private, through which an EV can be charged.
Combined Charging System (CCS): A device attached to the end of a power cord that connects to an EV. CCS is used in DC charging and can reach power levels of up to 350 kW.
CHAdeMO: A device attached to the end of a power cord that connects to an EV. This connecter, used for DC charging, can reach capacities up to 50 kW. Currently, CHAdeMO compatibility is found mainly on models from Asian manufacturers.
Direct Current (DC): An electrical current that flows in one direction. It is the type of current that comes from a battery. When being charged by alternating current (AC), EVs need to convert the power to DC to replenish their batteries.
Degradation: The loss of a battery’s ability to hold a charge. EV batteries degrade slowly, typically at a rate of 1% to 2% per year.
Direct to Consumer: When an automobile purchase occurs between a manufacturer and consumer, rather than through a dealership or third party.
Electric Vehicle (EV): A vehicle powered either partially or entirely by an electric battery.
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE): Infrastructure that supplies power to an EV. EVSE creates two-way communication between the charging station and EV that ensures the battery does not overcharge.
EPA Rated: The measurement of a vehicle’s efficiency as tested by the Environmental Protection Agency.
Emergency Roadside Service (ERS): A service that sends assistance to motorists when their vehicles suffer a mechanical failure or are otherwise inoperable.
Extreme Temperatures: Significantly high or low temperatures that have a negative effect on an EV’s efficiency.
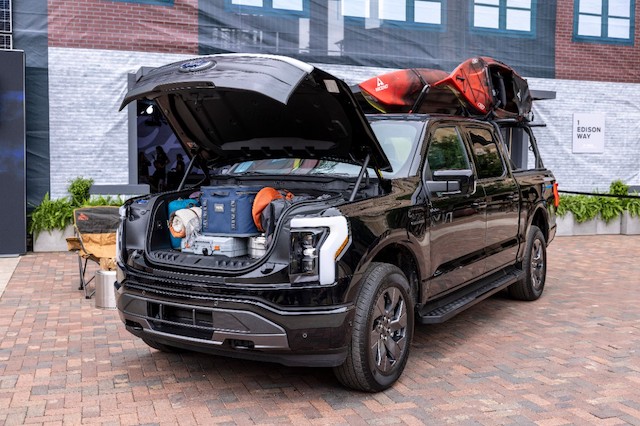

Frunk: A front storage space in EVs located in the area that houses the engine in gas-powered cars. The name is a portmanteau of “front” and “trunk.”
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles: Powered by hydrogen, these environmentally friendly cars produce no harmful emissions (just water vapor).
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Byproduct gases emitted by internal combustion engine cars that trap heat within Earth’s atmosphere, causing a greenhouse effect that contributes to climate change.
Home Charging Unit: A specialized charging device installed at a private residence. Many EV owners opt to upgrade to home charging units as they typically provide Level 2 charging, as opposed to the Level 1 charging of a household outlet.
Hybrid Electric Vehicle: A type of car that uses both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor for improved fuel economy.
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE): The gas-powered source of energy in traditional cars. Byproducts of an internal combustion engine include harmful emissions such as carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.
Incentive: Givebacks to purchasers of an EV and/or EV infrastructure. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, discounted toll fare, etc.
Inverter: A device in EVs that converts the battery’s direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) to power the motor.
Kilowatt (kW): A unit of electric power equal to 1,000 watts. It is used to measure the power generated by an EV’s battery.
Kilowatt hour (kWh): A unit of measurement for energy consumption showing how much power an energy source can provide in one hour.
Level 1 Charging: The slowest form of charging, Level 1 is usually done at home using a standard 120V household outlet. Level 1 charging takes several hours to fully replenish an EV battery.
Level 2 Charging: Level 2 charging is significantly faster than Level 1, adding roughly 20-50 miles of range per hour. Level 2 chargers need to be professionally installed to be used residentially. Most public charging stations are Level 2.
Level 3 Charging: Also known as DC (Direct Current) charging, Level 3 charging is capable of high-power energy transfer that can replenish an EV battery to 80% in a half-hour.
Lithium-Ion Battery: The type of battery used on most EVs due to its high energy density and ability to be continually recharged.
MPGe: MPGe, or Miles Per Gallon Equivalent, is a measure of an EV’s efficiency, used to compare to a gas-powered car’s MPG.
Neighborhood Electric Vehicle: A small, low-speed battery electric vehicle (BEV). They typically have a top speed of 25 mph and can be recharged through a standard outlet.
Noise Pollution: Any noise or sound emanating from an automobile. Since EVs do not have engines, they emit very little noise pollution.
On-Board Charger: A device found in EVs that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) to charge the battery.
Ohm: A unit of measurement of electrical resistance. Resistance affects a material’s ability to conduct electricity. Higher resistance creates a slower flow of electricity.
Ownership Options: The choice to buy or lease an automobile.

Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV): A type of hybrid car with batteries that can be charged externally (as opposed to traditional hybrids, which accumulate energy from features like regenerative braking).
Price Parity: When the price of two different commodities is the same. Price parity is often used in discussion of the cost comparison between EVs and gas-powered cars.
Powertrain: The set of components that generate energy and deliver that energy to a vehicle’s wheels. An electric powertrain consists mainly of a battery pack, energy converter and electric motor.
Qualified Plug-In Electric Drive Motor Vehicle: An EV that allows an owner to claim a tax credit for their purchase.
Range: The distance an EV can travel on a single full charge.
Range Anxiety: A motorist’s fear that they will run out of battery charge before reaching their destination.
Regenerative Braking: A system found in most EVs that captures the energy created by braking and transfers it to the car’s battery.

Supercharger: Tesla’s propriety EV charger that can only be used on Tesla vehicles. According to the automaker, these powerful chargers can add up to 200 miles of range in as little as 15 minutes. Tesla owns and operates a network of more than 35,000 superchargers across North America.
SAE J-1772: Also known as a J plug or Type 1 plug, it is the North American standard electrical connector for EVs.
State of Charge: The level of charge an EV battery has at any given time relative to its capacity.
Tax Credit: A financial incentive that subtracts the amount of the credit from a taxpayer’s federal or state tax bill.
Torque: A way to measure the force that causes objects to twist or rotate. Electric cars generally have high torque, giving them quick acceleration from a standstill.
Traction Motor: The motor found in an EV that uses power from the battery to drive the vehicle’s wheels, propelling the car forward.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): The complete financial cost of owning a vehicle, including, but not limited to, the price paid for the car, as well as registration, insurance, maintenance and energy costs.
Utility Rate: The retail cost of electricity. Utility rates vary by region and also fluctuate during peak and off-peak hours.
Vehicle Control Unit: The processing center of an EV, coordinating the vehicle’s power and motor control, regenerative braking, load management and power supply.
Volt: A unit that measures the flow of electrical current between two points. In regard to EV chargers, the higher the voltage, the faster the power is transferred to the battery.
Warranty: A contract issued to the purchaser of a vehicle guaranteeing the manufacturer will cover all repairs and/or replacements during a specified period of time.
Worldwide Harmonized Light Test Procedure (WLTP): A test measuring fuel consumption and emissions of passenger cars.
Yearly Maintenance: The inspection and, if necessary, repair of an automobile that should be done at least once per year by a qualified mechanic.
Zero Emissions Vehicle (ZEH): A vehicle that emits no exhaust gas or other pollutants while in use.
Type 1 Connector: A device attached to the end of a power cord that connects to an EV. Type 1 is a five-pin, AC plug. It is standard in the U.S. and can reach a charge of up to 7kW.
Type 2 Connector: A device attached to the end of a power cord that connects to an EV. Type 2 is a seven-pin, AC plug that can reach power levels of up to 22 kW at home and 43kW at a public charging station.
Visit AAA’s Electric Vehicle platform for more information on these cars of the future.