Environmentally friendly cars were all the rage until gas prices plummeted a couple of years ago. Nevertheless, many automakers still consider alternative fuels like hydrogen and electricity the waves of the not-so-distant future, and the emerging technologies are getting more and more innovative every day.
The problem is, unless you’re a rocket scientist or someone who reads about this stuff on a daily basis, it’s hard to keep track of the hodgepodge of car terms used to describe said automobiles. Read a car magazine today, and you’ll likely come across complex car terms like “PHEV” and “regenerative braking.” If you don’t know the vernacular, it can really worsen the experience.
What’s more, if you are considering an electric or hybrid car as your next every day commuter, it’s a good idea to know the lingo before you get to the dealership. Keep reading for a glossary of new-age car terms (which you can use to impress/annoy people at parties).
A glossary of car terms used to describe environmentally friendly cars
All-electric range: In a battery-powered electric car, the all-electric range is how far the vehicle can travel using just its battery, on a single charge.
Batteries: In electric cars, batteries power the propulsion of the vehicle. These are different than the starting, lighting and ignition (SLI) system batteries used in most automobiles (including electric ones).
Biofuels: These fluids are derived from renewable resources and used to power cars. Examples include, ethanol (made from corn, sugar cane and more), biodiesel (made form oils and fats) and bio-gas (methane made from the fermentation of organic matter).
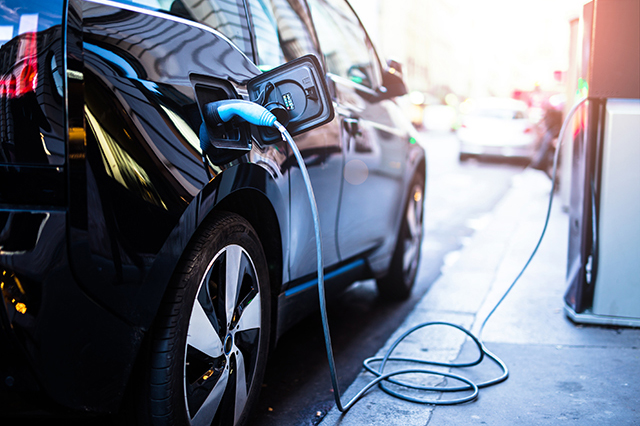
Charging: Pretty self-explanatory as far as car terms go, but plugging your car into a power source to replenish the battery power.
Charging station: Like a gas station, but for electric vehicles.
Clean diesel vehicles: A form of diesel fuel that contains 97 percent less sulfur, which significantly reduces harmful emissions.
Compressed air vehicles: Environmentally friendly cars powered by air stored in on-board canisters or tanks. Check out this one made from LEGOs.
Electric vehicle (EV): A battery-powered vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion.
Electric vehicle supply equipment: Another term for the wall chargers and charging stations used to power electric vehicles.
Electric motor: Motors that convert electricity into mechanical energy.
Fast chargers: A term used for high-power charging stations capable of returning an electric car battery back to 80 percent in a half-hour.
Flex-fuel vehicles: A type of vehicle that runs on more than one fuel, typically gasoline blended with ethanol or methanol.
Fuel cell electric vehicles: Powered by hydrogen, these environmentally friendly cars produce no harmful emissions (just water vapor). The Toyota Mirai and Hyundai Tucson are examples of hydrogen-powered vehicles available in the United States.
Home charging unit: An electric vehicle charger that can be mounted inside or outside one’s home.
Hybrid electric vehicle: A type of car that uses both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor for improved fuel economy.
Kilowatt hour (kWh): A unit of measurement for energy consumption, typically used to calculate the cost to refuel an electric car.
Level 1 (120V) charging: Basically, this car charging is done with your typical household power outlet. It is the slowest of the three levels of car charging, with a full charge sometimes taking upward of 20 hours.
Level 2 (240V) charging: The next step up as far as chargers go, with the ability to add about 70 miles of range per hour to your EV. Most public charging stations are Level 2.
Level 3 (480V) charging: The fastest of the three charging levels, and another term for the fast-chargers mentioned above.
MPGe: Like miles per gallon, but for alternative fuels and hybrid vehicles. It stands for miles per gallon equivalent.
Neighborhood electric vehicles: Smaller, battery powered electric vehicles with a top speed of 25 mph. Street legal in 46 states, most are relegated to roads with speeds limits under 45 mph.
Noise pollution: Excessive noise caused by machines and motor vehicles, which can be detrimental to health. Diesel engines are typically louder than petrol ones, and electric cars are quieter than both.

Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV): Hybrid cars with huge batteries that have to be charged from a power outlet or at a charging station (as opposed to traditional hybrids, which get the energy for their batteries from features like regenerative braking). There are two main types of plug-in hybrids. Those are:
- A) Extended-range plug-ins: In these cars, gasoline is only used once the battery is drained, and it only powers the electric motor.
- B) Parallel or blended plug-ins: In which both gasoline and electricity are used to propel the car most of the time (at slow speeds, it’s sometimes just the electric motor that makes the car go).
Powertrain: The powertrain of an automobile includes the engine, transmission, driveshaft, suspension and wheels. The Hyundai Ioniq is available with three electrified powertrains — hybrid, plug-in hybrid and all-electric.
Regenerative braking: A system in which the mechanical energy generated by physically braking is converted to electricity to power an electric motor.
Start/stop technology: A relatively new automotive feature that automatically shuts down (and starts) an idle engine to reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
Torque: A way to measure the force that causes things to twist or rotate. Some electric cars have 100 percent of their torque available at 0 rpm, which gives the strong and quick acceleration.
Volts: A unit that measures the flow of electrical current between two points. Some refer to it as “electrical pressure.” In regards to electric car chargers, the higher the voltage, the faster power is transferred to the battery.
Did we leave out any important car terms? Let us know in the comments section and we’d be happy to add them.
Also, if you’re in the market for environmentally friendly cars, be sure to check out AAA’s annual Green Car Guide. In it, you’ll find in-depth reviews of 81 of the most eco-friendly rides, plus you can read more about different green car types, get tips for buying used EVs and so much more.
Visit AAA’s Electric Vehicle platform for more information on these cars of the future.